Balanced Scorecard Example
The Balanced Scorecard framework is one of the simplest and most effective tools for aligning your organization’s most important objectives.
In this article, you will find:
- Balanced Scorecard Examples: Practical examples that demonstrate how to structure and implement a Balanced Scorecard in your organization.
- Balanced Scorecard Templates: Ready-to-use templates that you can build in KPI Fire, Excel, or PowerPoint to jump-start your strategic planning.
- Reasons to Use a Balanced Scorecard: Understand the benefits of using a Balanced Scorecard to align your team’s goals with your organization’s strategic vision.
By the end, you’ll have a clear path to creating a Balanced Scorecard that drives results and improves organizational performance.
What is the Balanced Scorecard Framework?
The Balanced Scorecard is a strategic management framework that helps organizations align their business activities with their vision and strategy. It balances traditional financial metrics with non-financial measures, focusing on four key areas: financial performance, customer satisfaction, internal processes, and learning and growth. By using this approach, organizations can monitor and improve performance across these areas, ensuring that short-term actions align with long-term objectives. The Balanced Scorecard transforms strategic goals into measurable outcomes, driving continuous improvement and better decision-making.

Download the free Balanced Scorecard Template…
Track strategy, align teams, and measure what matters.
- Track Strategy
- Align teams
- Measure what matters
- Organize objectives, KPIs, targets, and owners
- Use all four Balanced Scorecard perspectives
- Download in Excel
Read more about the Free Balanced Scorecard Template


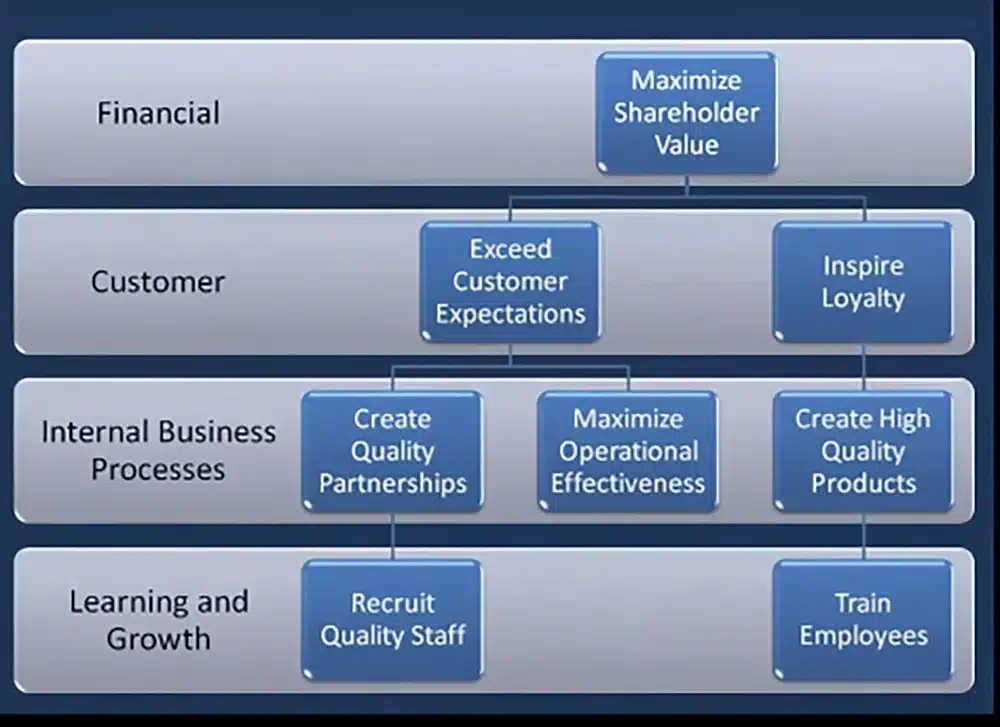
Understanding The Four Perspectives of a Balanced Scorecard
The typical balanced scorecard will have goals in each of the following “perspectives”
- Financial: These are financial goals, usually lag measures such as Revenue, Ebita, or Growth.
- Customer or Stakeholder: These are goals to help focus on the outcomes that your customers or stakeholders receive. Common goals here are about market share, or customer happiness or loyalty, such as Net Promoter Score.
- Business Process Goals: These are goals focused on the “how” you go about achieving the Financial & Customer goals. This is where most Operational Excellence, or Process Improvement goals belong.
- Organization Capacity/Learning & Growth/Culture: These goals typically refer to employee happiness, or employee development, or goals to develop certain capabilities as an organization.
The typical balanced scorecard will have goals in each of the following “perspectives”:
1. Financial Perspective
The financial perspective is a major focus of the balanced scorecard. It addresses the key questions:
- Are you making money?
- Are you achieving your financial goals?
Common Goals: Growth, Financial Success.
Common Metrics: Revenue, Profit, Ebitda, Contribution Margin
2. Customers Perspective
Additionally, the customer perspective focuses on the people who actually buy your products and services.
- Are you winning new business?
- How about keeping your existing customers happy?
- How are you viewed in your industry compared to your competitors?
- Are your customers getting value from your solutions?
Common goals here are “Winning with Customers” or customer happiness and loyalty, such as Net Promoter Score.
Common Metrics: Customer Loyalty, # of Customers, Net Promoter Score
3. Internal Processes Perspective
This perspective is all about how efficiently each of your business processes are running. These are about reducing waste, speeding things up, and doing more with less.
- Are there unneeded obstacles standing between new ideas and execution?
- How quickly can you adapt to changing business conditions?
- Are we operating with excellence in our processes?
These internal processes perspective goals are the drivers of the success in your Customer and Financial perspectives.
This perspective is critical for balancing the flow of value to your customers. If these Internal processes are running efficiently, you should be delivering value to Customers.
Common Goals: Operational Excellence
Common Metrics: Capacity Utilization, OEE,
4. Culture / Learning and Growth
The learning and growth perspective looks at your overall corporate culture, and how well you are setup for the future. Many companies consider future capabilities and innovation an important aspect of this pillar.
- Are people aware of the latest industry trends?
- Is it easy for employees to share knowledge?
- Does everyone have access to training and continuing education?
Technology also plays a major role in learning and growth.
- Are people able to use the latest devices and software, or are your archaic systems stuck running yesterday’s tech?
- What are you doing to make sure your organization is staying ahead of your competition?
Goals in this perspective typically refer to employee happiness, employee development, or goals to develop certain capabilities as an organization.
Balanced Scorecard Template
Balanced Scorecard Examples for Various Industries
Balanced Scorecard Examples for Manufacturing
- Financial
- Goal: Growth
- Metric: Profit margin percentage
- Customer
- Goal: Winning with customers
- Metric: On-time delivery rate
- Internal Processes
- Goal: Streamline production process
- Metric: Production cycle time, First Time Right %,
- Learning & Growth
- Goal: Improve worker safety
- Metric: Safety training hours per employee, Investments in Innovation
Balanced Scorecard Examples for Retail
- Financial
- Goal: Growth
- Metric: Year-over-year sales growth
- Customer
- Goal: Winning with customers
- Metric: Customer retention rate
- Internal Processes
- Goal: Optimize inventory management
- Metric: Inventory turnover ratio
- Learning & Growth
- Goal: Upskill sales associates
- Metric: Sales training completion rate
Balanced Scorecard Examples for Healthcare
- Financial
- Goal: Growth
- Metric: Increase in Revenue
- Customer
- Goal: Improve patient outcomes
- Metric: Patient satisfaction score
- Internal Processes
- Goal: Reduce wait times
- Metric: Average patient wait time
- Learning & Growth
- Goal: Advance medical staff skills
- Metric: Certification completion rates
As of 2022 KPI Fire offers a NEW version of Balanced Scorecard, Check out this post for more info.
Once you’ve decided on the objectives for your Balanced Scorecard, KPI Fire software can be used to build your scorecard and to get the right performance information to the right people. KPI Fire adds structure and discipline to share and implement the Balanced Scorecard system, helps to transform disparate corporate data into information and knowledge, and helps communicate performance information.
The KPI Fire model encourages users to ask 3 key questions in this planning process.
- What do we want to accomplish: (This is the Goal)
- How will we measure it? (The Metric is a measurable number that will tell us when we achieve the number.)
- What work needs to be done (These are the Projects).
Part 2: Conducting the Monthly Strategy Review
Preparation: A few days to a few hours before the meeting. Consequently, prior to the strategy review meeting each metric owner should update the metrics that they own.
Here are a few tips to accomplish this:
Preparation
Unfortunately, companies spend time developing annual strategic plans. However, few really excel at managing to the plan. Surprisingly, the monthly strategy review is where you can really make progress on your goals presently. Secondly, you can find out where things may be falling short so you’ll have time to take a corrective action.
- Establish Red/Amber/Green zones for metrics straightaway.
- Meanwhile, gather your Metric data prior to the meeting.
- Explicitly separate Projects (stuff you are doing), from the Metrics (what you will measure).
- Markedly, celebrate the “Green”, and spend time on the Red/Amber.
- Have a conversation. The purpose of the strategy review is to bring potential issues to the surface and especially make plans to resolve them.
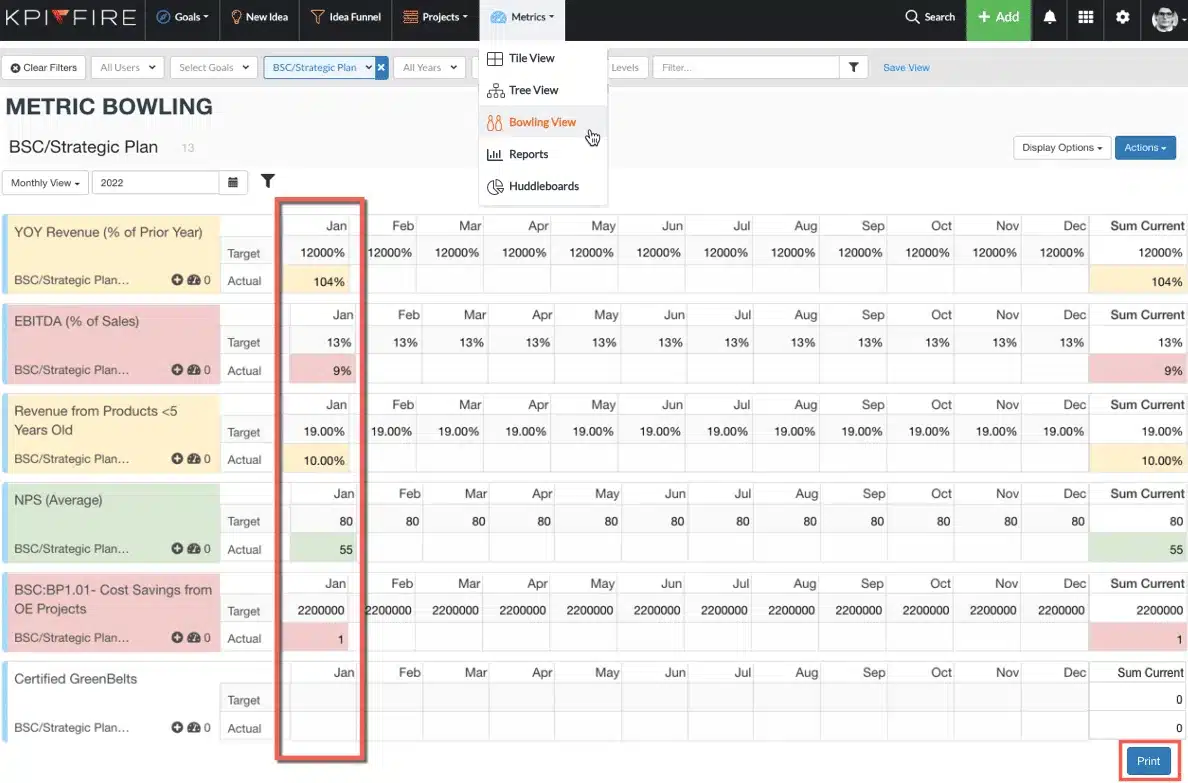
- Consequently, use the Metric > Bowling View to determine if your values have been updated for a given month. If you are comfortable working from the web interface, then go for it! Alternatively, if you would be more comfortable printing out the pages, use the print option.
For the Balance Scorecard Example Review Meeting
If you would like to use the live software for your BSC strategy review:
- Locate & Select your Saved View
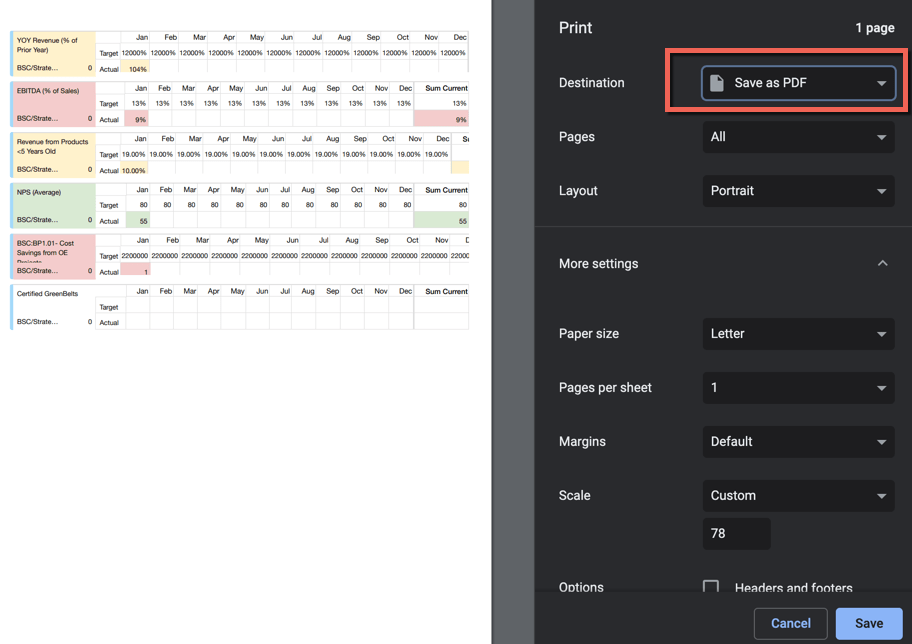
If you prefer to print or send out a PDF, then you can use the print option at the bottom.
As a result, tips for your Balanced Scorecard Example Review meetings:
1- Use this time to confirm if the right goals, metrics, and projects are listed straightaway. If there is a goal that has changed, or consequently, a project that has been killed, this is a great time to make sure everyone is made aware.
2- Celebrate successes, but spend your time focusing on the Red & Yellows. Each item in KPI Fire will have a Red/Yellow, or Green indicator. The majority of the time you have allocated for the review should be spent discussing what to do about KPIs that are not on track.
3- Create corrective actions as new projects. If you have a metric that is significantly off track, then you may need to create a new project as a corrective measure. Not only can create the project during or after the meeting, but also make sure it shows up in time afterwards.
4- Expect Changes: accordingly, the data in the BSC may or may not be 100% accurate. The attendees at the meeting may not always agree on the status of a vague KPI. The most valuable part of the meeting is in the dialogue that is consequently generated.

Turn Ideas into Measurable Business Results - Book Your Free Demo Today!
Join world-class companies that have tracked and saved over $1.4 Billion with KPI Fire.
- Track Cost Savings & ROI in Real Time
- Align Strategy with KPI Metrics
- Drive Execution & Engage Teams
Schedule a 30-minute demo to discover how KPI Fire can boost your business.